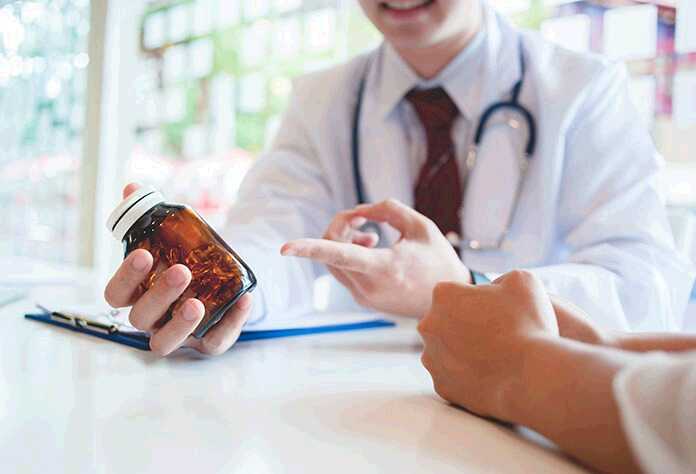
If you have diabetes, managing your condition is important to living a healthy and active life. Lifestyle changes and drug therapy are some of the main components to managing diabetes. However, medication options differ depending on the type of diabetes you have.
Diabetes Treatment Considerations
In Type 1 diabetes, the body doesn’t produce insulin, so injections of this hormone are necessary. On the other hand, for Type 2 diabetes, the body produces insulin but no longer uses it well. So, Type 2 diabetics may have combination drug therapy with or without insulin injections.
Some medications help manage blood sugar directly by stimulating the pancreas to make more insulin or inhibiting the liver to make less glucose. Doctors may also prescribe combination drug therapy that also addresses serious health risks associated with diabetes like high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
Furthermore, some medications are available in both oral and injection forms. But some drug therapies, like insulin, are only available through injections. Doctors generally take patient preference into consideration – unless injections are a necessary part of the therapy.
Weight, age, A1C, and overall lifestyle are other factors that doctors take into consideration when prescribing diabetesmedications.
The Best Medications for Diabetes
Diabetes medications available for prescription are for Type 2 diabetics to control blood sugar levels. There are 9 medication categories, and doctors may prescribe a combination of them for better blood sugar management.
1. Biguanides: lowers the amount of sugar made by the liver
The most common form is metformin:
- Metformin Hydrochloride ER
- Glucophage
- Riomet
- Glumetza
- Fortamet
It is also used in combination with other drugs such as:
- glipizide
- empagliflozin [Synjardy]
- canagliflozin [Invokamet]
- dapagliflozin [Xigduo XR]
- alogliptin [Kazano]
- saxagliptin [Kombiglyze XR]
- rosiglitazone [Avandamet]
- repaglinide [PrandiMet]
- sitagliptin [Janumet]
- glyburide [Glucovance]
- pioglitazone [Actoplus]
- linagliptin [Jentadueto]
Keep in mind, however, that all of these combination drugs are preceded by “metformin” and followed by a hyphen.
2. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors: assists with breaking down table sugar and starchy foods
This type of drugs typically requires you to eat a meal afterward:
- acarbose [Precose]
- miglitol [Glyset]
3. DPP-4 inhibitors: help the body make insulin
Drugs that help the pancreas make insulin includes:
- alogliptin-metformin [Kazano]
- linagliptin-metformin [Jentadueto]
- saxagliptin [Onglyza]
- saxagliptin-metformin [Kombiglyze XR]
- sitagliptin [Januvia]
- sitagliptin-metformin [Janumet and Janumet XR]
4. Dopamine agonists: may prevent insulin resistance
Bromocriptine (Cycloset) is a type of dopamine agonist that may lower blood sugar levels by boostingdopamine in the body.
5. Meglitinides: helps the body release insulin
These drugs may lower blood sugar levels too much, but they may be necessary as determined by the doctor:
- repaglinide-metformin
- nateglinide
- repaglinide
Or you may recognize the drug’s trade names:
- Prandimet
- Starlix
- Prandin
6. Glucagon-like peptides (incretin mimetics): increase B-cell growth and insulin use
This type of drug may also help decrease appetite and slow the rate of your stomach emptying. They include:
- exenatide [Byetta]
- exenatide extended-release [Bydureon]
- dulaglutide [Trulicity]
- liraglutide [Victoza]
7. Sulfonylureas: stimulate the pancreas to make more insulin
These medications include:
- tolazamide
- tolbutamide glipizide-metformin
- glyburideg lyburide-metformin
- chlorpropamide glimepiride-pioglitazone
- glipizide
- glimepiride-rosiglitazone
Some of the trade names for these pancreas-stimulating medications may be more recognizable:
- Orinase, Tol-Tab
- Diabinese
- Avandaryl
- Glucovance
- DiaBeta
- Glynase
- Micronase
- Duetact
- Metaglip
- Tolinase
- Glucotrol
8. Sodium glucose transporter (SGLT) 2 inhibitors: encourage the kidneys to release excess glucose
Medications that fall under this category include:
- empagliflozin-linagliptin
- empagliflozin-metformin
- canagliflozin-metformin
- empagliflozin
- ertugliflozin
- dapagliflozin
- dapagliflozin-metformin
- canagliflozin
However, you may be more familiar with their trade names:
- Glyxambi
- Synjardy
- Invokamet
- Jardiance
- Steglatro
- Farxiga
- Xigduo XR
- Invokana
9. Thiazolidinediones: Help fat cells use insulin more efficiently
These medications also decrease glucose in the liver:
- Duetact
- Actoplus Met, Actoplus Met XR
- Amaryl M
- Actos
- Oseni
- Avandia
- Avandaryl
You may also see these medications listed under their formal names:
- pioglitazone-glimepiride
- pioglitazone-metformin
- rosiglitazone-metformin
- pioglitazone
- pioglitazone-alogliptin
- rosiglitazone
- rosiglitazone-glimepiride
Other Medications
Not all diabetic medications fall under these categories. Sometimes Type 1 and Type 2 diabetics need other medications to treat conditions that arise from diabetes. They include:
- high cholesterol drugs
- aspirin for heart health
- high blood pressure medications
Final Thought
There’s a wide range of medications for diabetes. Some people don’t use medications at all. But it depends on your situation. In the end, it’s best to decide with your doctor whether you should manage diabetes with medications.